ADVERTISING
Get Free Live 2022 NABTEB May/June Agricultural Science Paper II (Practical) Questions and Answers for School Candidates Free of Charge | NABTEB May/June Free Agric Science Paper II (Practical) Questions and Answers EXPO Room (7th July, 2022).
NABTEB MAY/JUNE 2022 FREE AGRIC PRACTICAL QUESTION AND ANSWER ROOM [NBC/NTC]
Thursday 7th July, 2022
Agricultural Science Paper II (Practical) 9:00a.m-11.00a.m (2hrs)
Agricultural Science Paper II (Practical) 9:00a.m-11.00a.m (2hrs)
2022 NABTEB AGRIC PRACTICAL ANSWERS:
B is formed from accumulation of sediments
D is formed from the cooling and solidification of molten magma.
(1aii)
Specimen B:
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i) sandstone
(ii) breccia
(iii) shale
(iv) conglomerate
Specimen D
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i) granite
(ii) gabbro
(iii) diorite
(iv) basalt
(1aiii)
Difference between B and D:
Specimen B:
(i) Contains Fossil
(ii) Less crystal line
(iii) Formed from accumulation of sediments.
Specimen D:
(i) Does not contain fossil
(ii) Contains large crystals.
(iii) Formed from cooling and solidification of magma.
(1c)
(i) The breakdown of specimen D into smaller fragment forms soil which help in crop planting.
(ii) Boulders and granite from specimen D can help in construction of farm buildings.
(1d)
(i) The abundance of specimen D can cause acidity.
(ii) The soil must be overly loose when D is abundant and hence reduce water retention capacity.
(iii) The abundance of D will increase toxicity and prevent organic matter formation.
=======================================================
(2a)
Specimen F - Knapsack sprayer
(2b)
(i) Hand sprayer
(ii) Bucket sprayer
(iii) Truck-bed sprayer
(2c)
(i) Protective cover should be put on to prevent inhalation of chemicals.
(ii) Do not spray against wind direction.
(iii) The nozzle should not be blown with mouth.
(iv) Avoid smoking or eating during spraying.
(v) Washing of hands thoroughly after spray.
(2d)
Fill up the sprayer with water, addition of measured amount of the herbicide or insecticide. Cover the sprayer and shake vigorously. Spray through the nozzle by applying pressure on the switch.
(2e)
(i) Nozzle may be blocked by soil
(ii) The switch may malfunction due to excessive use.
(iii) There may be leakage due to crack
====================================================
(3a)
G - Pepper fruit
H - Onion bulb
I - Cotton seeds
K - Okra seeds
(3b)
SPECIMEN G-
[Pick any ONE]
(i) Used as yolk colourant,
(ii) Source of antioxidant (piperine),
(iii) Used in tear gas to disperse crowds/ as pepper spray.
(iv) Spice for food
-SPECIMEN H-
[Pick any ONE]
(i) Sources of vitamins A and C.
(ii) For flavouring food
(iii) Medicinal uses.
(iv) Source of volatile oil
(3c)
-SPECIMEN H - Spices
-SPECIMEN I - Fibre
-SPECIMEN K - Vegetable
(3d)
Climatic and soil requirements:
Specimen G needs a moderate winter climate with about bout 2000 mm rain annually.
The soil should have a good structure and water-holding capacity. Drainage must be good to prevent root rot. The pH should be 5,5 to 6,0.
Propagation: Propagation is usually by means of cuttings. One or two-leaf cuttings are taken only from secondary runners during September. Cuttings are rooted in mistbeds and transplanted into the land after
9 months.
Spacing: Spacing between the rows is 3 m and between the plants 2 m, which gives
1 666 plants/ha.
Trellising: Because pepper is a climbing vine, provision must be made for supports.
Fertilisation: Pepper plants react very well to organic fertilisation. Magnesium must be applied in the form of magnesium sulphate at about 750 g per plant .
Mulching: Pepper plants have a shallow root system. The use of an organic soil cover is therefore very beneficial.
Irrigation: Overhead irrigation is preferred to flood irrigation.
Harvesting: After flowering, it takes about 9 months before the ripe berries can be picked.
(3e)
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i) Onion thrips
(ii) Onion maggot
(iii) Bulb mite
============================================================
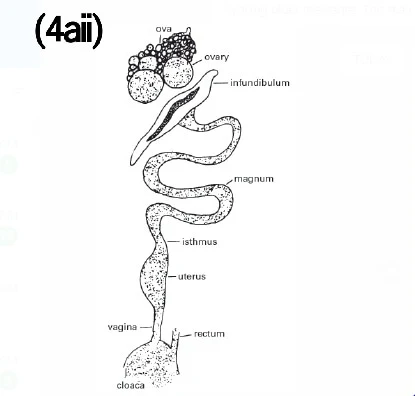
(4ai)
Oviduct of a hen
(4aii)
(4b)
(i) Infundibulum
(ii) Magnum
(iii) Isthmus
(iv) Vagina
(v) Cloaca
(vi) Uterus
(vii) Rectum
(i) Infundibulum: It enclosed the released yolk. It is the site of fertilizer.
(ii) Magnum: It is the site of albumin and chalaza production.
(iii) Isthmus: The shape of the egg is determined in the isthmus.
(iv) Vagina: This is the site deposition of sperm
(v) Cloaca: It extends out to expel egg through the vent
(vi) Uterus: The uterus or shell gland of the left oviduct is responsible for the formation of the eggshell
(vii) Rectum - It serves as a temporary store of faeces
(i) Infundibulum
(ii) Magnum
(iii) Isthmus
(iv) Vagina
(v) Cloaca
(vi) Uterus
(vii) Rectum
(i) Infundibulum: It enclosed the released yolk. It is the site of fertilizer.
(ii) Magnum: It is the site of albumin and chalaza production.
(iii) Isthmus: The shape of the egg is determined in the isthmus.
(iv) Vagina: This is the site deposition of sperm
(v) Cloaca: It extends out to expel egg through the vent
(vi) Uterus: The uterus or shell gland of the left oviduct is responsible for the formation of the eggshell
(vii) Rectum - It serves as a temporary store of faeces
TO SUBSCRIBE FOR NABTEB AGRIC PRACTICAL ANSWERS VIA LINK
- JUST GO OUT AND BUY MTN CARDS OF N400 (200+ 200 = 400)
- GO TO YOUR MESSAGE, TYPE THE CARD PINS CORRECTLY AND SEND TO 08107431933.
- DON'T CALL, JUST TEXT, IF THE CARDS PINS ARE VALID, A REPLY WILL BE SENT TO YOU CONFIRMING THAT YOU HAVE BEEN SUBSCRIBED.
- RELAX AND WAIT FOR YOUR ANSWERS 30MINUTES BEFORE EXAM STARTS OR AFTER EXAM STARTS.
- NB: DO NOT SEND USED CARD PINS OR YOUR NUMBER WILL BE BLACKLISTED.
NB:
Only Share this Page with Trusted Students, We will be hiding this page
immediately exam ends and a new page will be created for the upcoming
exam. Kindly do well to bookmark the site and check back later.
===============================================
DAILY SUBSCRIPTION - PER SUBJECTS
*******Direct Mobile Payment Per Subject: N600***** [Gets Answers On Time]
******Direct Mobile Payment Per Practical: N400***** [Gets Answers On Time]
===========================================
===============================================
DAILY SUBSCRIPTION - PER SUBJECTS
*******Direct Mobile Payment Per Subject: N600***** [Gets Answers On Time]
******Direct Mobile Payment Per Practical: N400***** [Gets Answers On Time]
===========================================


![2022 NABTEB Agric Practical Answers [7th July] 2022 NABTEB Agric Practical Answers [7th July]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgoPebLYKGqEgaTEsZs4Qa_6XPN0eih39H7TOeZASZqgMkIbGB6kV6Nc_lMZ0zVMufJDl3TzIJteXlyigXDc6pXJo5P2_zA09pU0U5WwZmiEWcYV3I38tGspesuGNlwBScb2VN53xqbkO0/w320-h320-rw/NABTEB+Nigeria.jpg)
0 Comments
NOTE: Comments are moderated and may not appear immediately as they require review and approval by a moderator. Remember to check the "Notify Me" box before submitting your comment to receive notifications when your comment is approved or when a reply is posted.